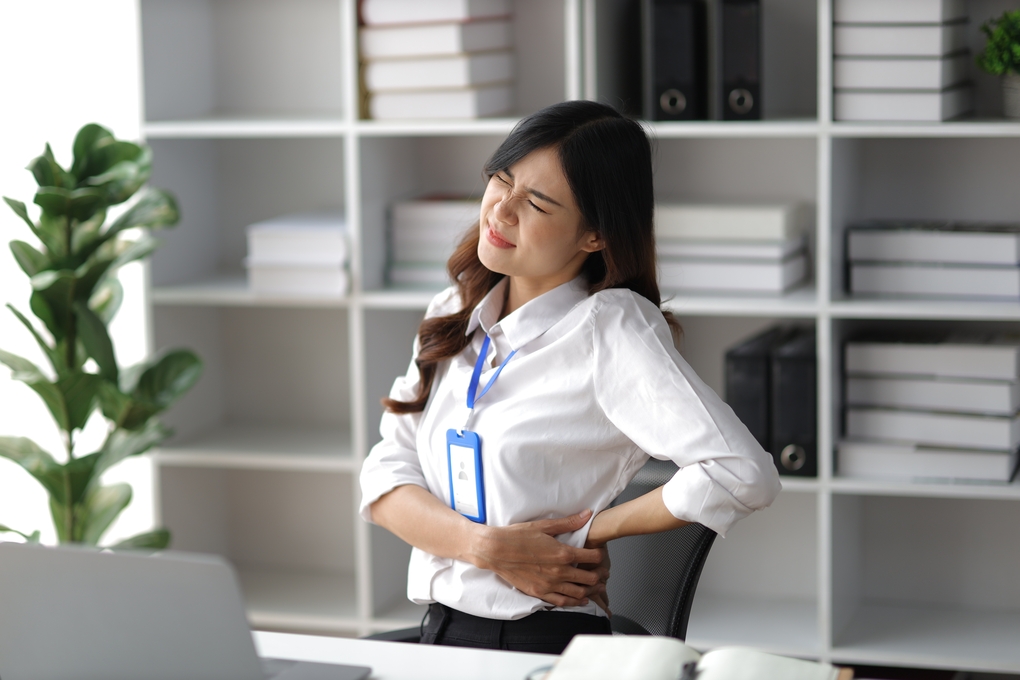

Back pain is among the most common health issues individuals face today, especially among working professionals. Sitting for long hours, poor posture, and work-related stress are often the key contributors. If you’re struggling with back pain, this blog will help you find the causes, its connection with work, and how physiotherapy can be an effective solution.
Understanding Back Pain
Back pain can affect anyone, irrespective of age or occupation. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, impacting a person’s daily routine and productivity.

Common Causes of Back Pain
- Poor Posture: Sitting for long hours, especially with poor posture, puts pressure on the spine, leading to back pain.
- Lifting Heavy Objects: Jobs that require lifting without proper technique can strain the back muscles.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity weakens the muscles supporting the spine, making the back more vulnerable to pain.
- Stress: Emotional stress can cause tension in the back muscles, leading to discomfort or pain.
- Injury: Accidents or falls can lead to back injuries, which may cause long-term pain if not treated properly.
Common Back Pain Conditions
Certain medical conditions can contribute to chronic back pain. These include:
1. Lumbar Back Pain
Pain in the lower back is the most common type of back pain.
2. Herniated Disc
A herniated disc occurs when one of the spinal discs slips out of place, causing pressure on the nerves. This can result in severe pain, especially in the lower back.
3. Sciatica
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed, usually due to a herniated disc. This can cause sharp pain radiating from the lower back to the legs.
4. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves abnormally. This can cause back pain, particularly after standing or sitting for long periods.
Back Pain and Work
Back pain can significantly impact work productivity. It can make concentrating, sitting for long periods, or lifting heavy objects difficult. If you’re experiencing back pain, it’s important to address it so that it doesn’t interfere with your work performance.

How Work Contributes to Back Pain
- Sedentary Jobs: Office workers often sit for extended periods, leading to poor posture and back strain.
- Manual Labor: Jobs that involve heavy lifting, bending, or twisting can strain the back muscles, resulting in injuries.
- Repetitive Movements: Repeated motions, especially without breaks, can cause strain and eventually lead to chronic back pain.
- Workplace Ergonomics: Poor workplace ergonomics, such as improper desk height or chair support, can contribute to the development of back pain over time.
Back Pain and Stress
Stress affects mental and physical health. Back pain and stress are closely related. When you’re stressed, your muscles tend to tense up, including those in your back. Chronic stress can cause the muscles to remain tense for extended periods, leading to persistent pain.
Back Pain Prevention Tips
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some simple yet effective tips to prevent back pain, especially for those with desk jobs or physically demanding work.
1. Maintain Proper Posture
Always ensure that you are sitting with your back straight, feet flat on the ground, and elbows at a 90-degree angle. Avoid slouching or leaning forward while working.
2. Take Regular Breaks
Take short breaks every 30 minutes to stand, stretch, or walk. This reduces strain on your back muscles and improves circulation.
3. Stay Active
Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen the muscles supporting your spine. This could include walking, swimming, or yoga.
4. Use Ergonomic Furniture
Invest in ergonomic chairs and desks that support good posture. Ensure your computer screen is at eye level to avoid straining your neck and back.
5. Lift Properly
When lifting objects, always bend your knees, keep the object close to your body, and avoid twisting your back.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Back Pain Management
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing and treating back pain. Whether the pain is acute or chronic, physiotherapy offers personalised treatment plans designed to address the root cause of the pain and prevent its recurrence.

When to See a Physiotherapist
It is essential to consult a physiotherapist if:
- You experience persistent back pain that lasts for more than a few days.
- Your back pain is affecting your ability to work or perform daily tasks.
- You experience tingling or numbness in your back, legs, or arms.
- Your back pain is the result of an injury.
How Physiotherapy Can Help
Physiotherapy for back pain typically includes a range of treatments and exercises designed to alleviate pain and improve mobility. The physiotherapist will conduct an initial assessment to determine the cause of your back pain and then develop a customised treatment plan.

1. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques like massage and joint mobilisation to relieve pain and improve mobility. This can help release tension in the muscles and improve blood flow.
2. Exercise Therapy
A physiotherapist will guide you through exercises designed to strengthen the muscles supporting your spine. These exercises focus on improving flexibility, posture, and overall strength, reducing the risk of future pain.
3. Posture Training
Poor posture is one of the leading causes of back pain. Physiotherapy includes posture training, which helps you adopt and maintain proper posture, both at work and in daily activities.
4. Education and Prevention
Physiotherapists provide education on preventing back pain, including ergonomic advice, safe lifting techniques, and tips for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
5. Pain Relief Techniques
Physiotherapists use various techniques, such as heat therapy, cold therapy, and electrical stimulation, to relieve back pain. These methods can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Conclusion
Back pain is a common problem that can significantly impact work performance and quality of life. Physiotherapy offers a range of treatments that address the root cause of back pain, providing long-term relief. Whether your back pain is caused by poor posture, repetitive movements, or an injury, consulting a physiotherapist can help you manage the pain effectively.
If you’re struggling with back pain, don’t wait until it gets worse. Physiotherapy can provide the support and treatment you need to recover and prevent future episodes of pain. Prioritise your health by seeking professional help and making necessary lifestyle changes today.
Physiotherapy can help you stay pain-free and productive at work by reducing back discomfort, enhancing your general well-being, and helping you with your posture.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Yes, physiotherapy can significantly help manage back pain. It helps improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and address the root cause of the pain through personalized exercises and treatment plans.
The best therapy for back pain depends on its cause and severity. Physiotherapy, which includes manual therapy, exercises, and posture training, is highly effective. Other options include chiropractic care, acupuncture, and pain-relief medication.
When you hurt your back at work, stop any activity that worsens the pain. Apply ice to the affected area, and if the pain persists, see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. You may also want to inform your employer about the injury, especially if it’s work-related.
The fastest way to fix a back strain is to rest, apply ice or heat, and gently stretch the affected muscles. Over-the-counter pain relief can also help. If the pain persists, consult a physiotherapist to guide you through recovery exercises.
The fastest way to fix a back strain is to rest, apply ice or heat, and gently stretch the affected muscles. Over-the-counter pain relief can also help. If the pain persists, consult a physiotherapist to guide you through recovery exercises.
To avoid back pain during work, maintain proper posture, take regular breaks to stretch, and use ergonomic furniture. Incorporating exercises that strengthen your core and back muscles can also help prevent discomfort.
If you’re working with lower back pain, try adjusting your workstation to support good posture. Take frequent breaks to move and stretch, and avoid heavy lifting. If possible, consult a physiotherapist to develop exercises that help alleviate your discomfort.
It depends on the severity of your back pain. If your pain is mild, staying active and maintaining movement can actually help. However, if the pain is severe or affecting your ability to function, you may need to take some time off and consult a healthcare professional for advice.

 Development
Development QLS
QLS Business
Business Healthcare
Healthcare Health & Fitness
Health & Fitness Technology
Technology Teaching
Teaching Lifestyle
Lifestyle Design
Design



0 responses on "Back Pain and Work: How Physiotherapy Can Help"